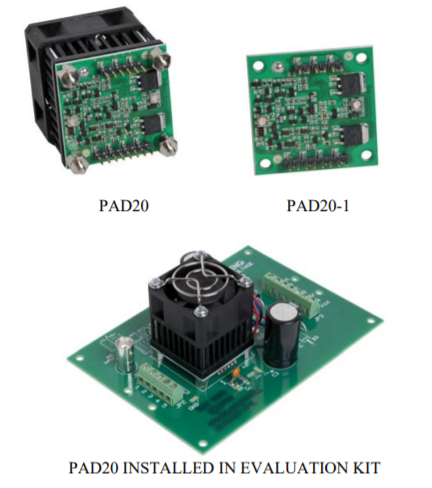
PAD20
KEY FEATURES
- LOW COST
- HIGH VOLTAGE – 150 VOLTS
- HIGH OUTPUT CURRENT – 5A
- 40 WATT DISSIPATION CAPABILITY
- 80 WATT OUTPUT CAPABILITY
- INTEGRATED HEAT SINK AND FAN
- SMALL SIZE – 40mm SQUARE
- RoHS COMPLIANT
APPLICATIONS
- SMALL MOTOR DRIVE
- HIGH VOLTAGE INSTRUMENTATION
- SEMICONDUCTOR TESTING
DESCRIPTION
The PAD20 high voltage operational amplifier is constructed with surface mount components to provide a low cost solution for many industrial applications. With a footprint only 40mm square, similar to the footprint of the TO3 hybrid package, the PAD20 offers outstanding performance that outperforms the more expensive hybrid amplifiers. External compensation tailors the amplifier’s response to the application requirements. Four wire programmable current limit is built-in. The PAD20 also features a substrate temperature reporting output and over-temp shutdown. The amplifier circuitry is built on a thermally conductive but electrically insulating metal substrate mounted to an integrated heat sink and fan assembly. No BeO is used in the PAD20. The PAD20-1 is also available without the integrated heat sink and fan for custom applications.
A NEW CONCEPT
A critical task in any power amplifier application is cooling the amplifier. Until now component amplifier manufacturers often treated this task as an after-thought, left for the user to figure out. At Power Amp Design the best heat sink and fan is chosen at the start and becomes an integral part of the overall amplifier design. The result is the most compact and volumetric efficient design combination at the lowest cost. In addition, this integrated solution concept offers an achievable real-world power dissipation rating, not the ideal rating usually cited when the amplifier case is somehow kept at 25℃. The user no longer needs to specify, procure or assemble separate components.
CIRCUIT & CONNECTIONS
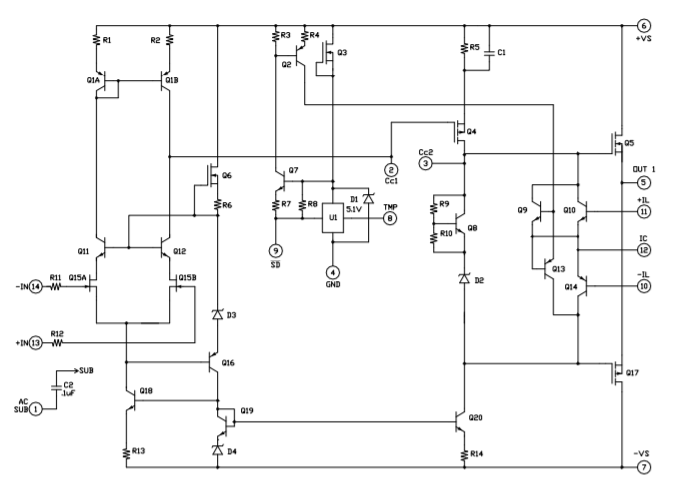
EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT
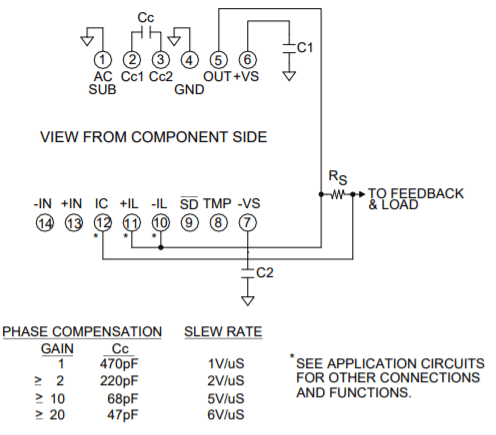
PINOUT & CONNECTIONS
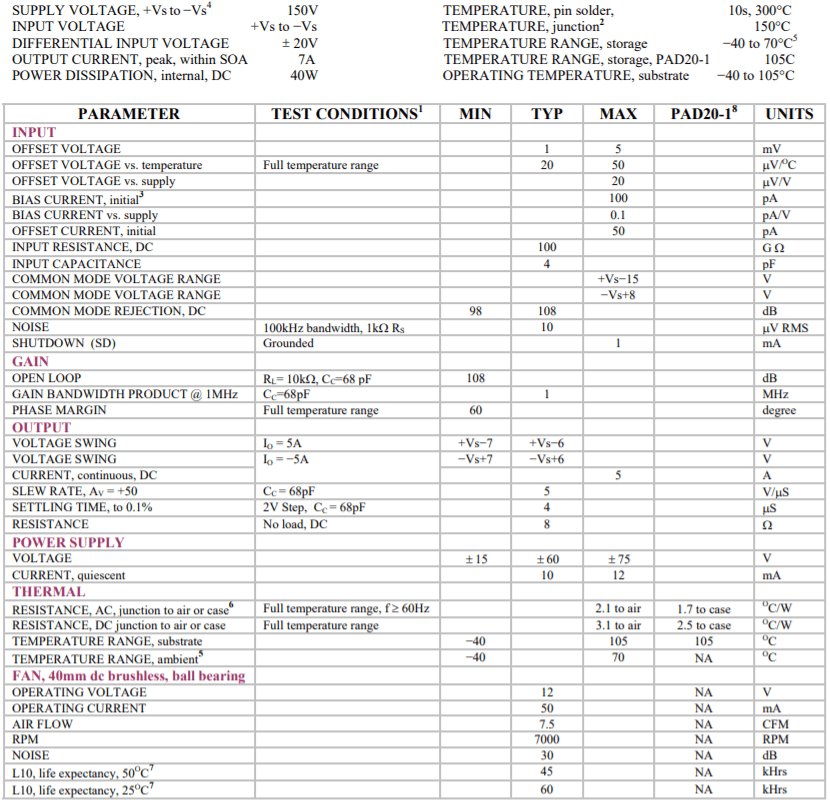
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS SPECIFICATIONS
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
NOTES:
- Unless otherwise noted: TC = 25℃, compensation Cc = 100pF, DC input specifications are +- value given, power supply voltage is typical rating.
- Derate internal power dissipation to achieve high MTBF.
- Doubles for every 10℃ of case temperature increase.
- +Vs and −Vs denote the positive and negative supply voltages.
- Limited by fan characteristics. During operation, even though the heat sink may be at 85℃ the fan will be at a lower temperature.
- Rating applies if the output current alternates between both output transistors at a rate faster than 60Hz.
- L10 refers to the time it takes for 10% of a population of fans to fail. Lower ambient temperature increases fan life.
- Specifications for the PAD20-1 are the same as for the PAD20 except as shown in this column.
OPERATING CONSIDERATIONS
COOLING FAN
The PAD20 relies on its fan for proper cooling of the amplifier. Make sure that air flow to the fan and away from the heat sink remains unobstructed. To eliminate electrical noise created by the cooling fan we recommend a 47µF capacitor placed directly at the point where the fan wires connect to the PCB. See application note AN-24 for further details.
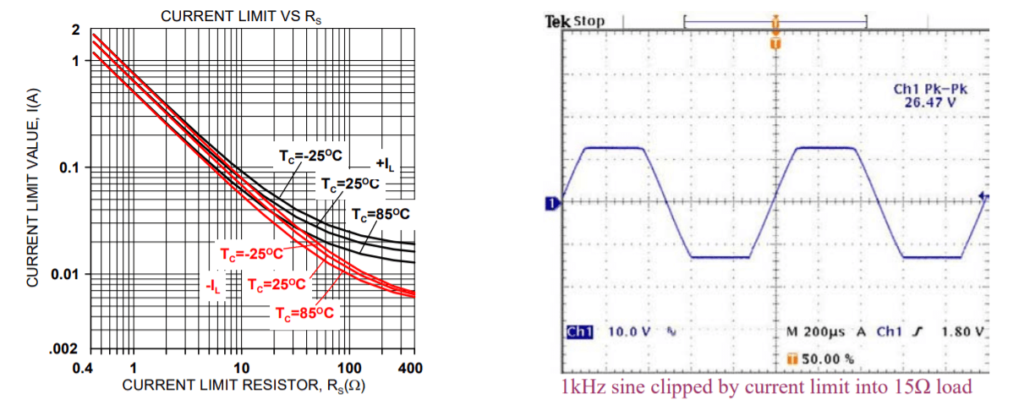
CURRENT LIMIT
The current limiting function of the PAD20 is a versatile circuit that can be used to implement a four-wire current limit configuration or, in combination with some external components can be configured to implement a fold-over current limit circuit. The four-wire current limit configuration insures that parasitic resistance in the output line, Rp, does not affect the programmed current limit setting. See Figure 1. The sense voltage for current limit is 0.63V. Thus approximately:
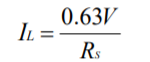
Where IL is the value of the limited current and Rs is the value of the current limit sense resistor from 0.4Ω-40Ω. See graph for Current Limit Value vs Rs.
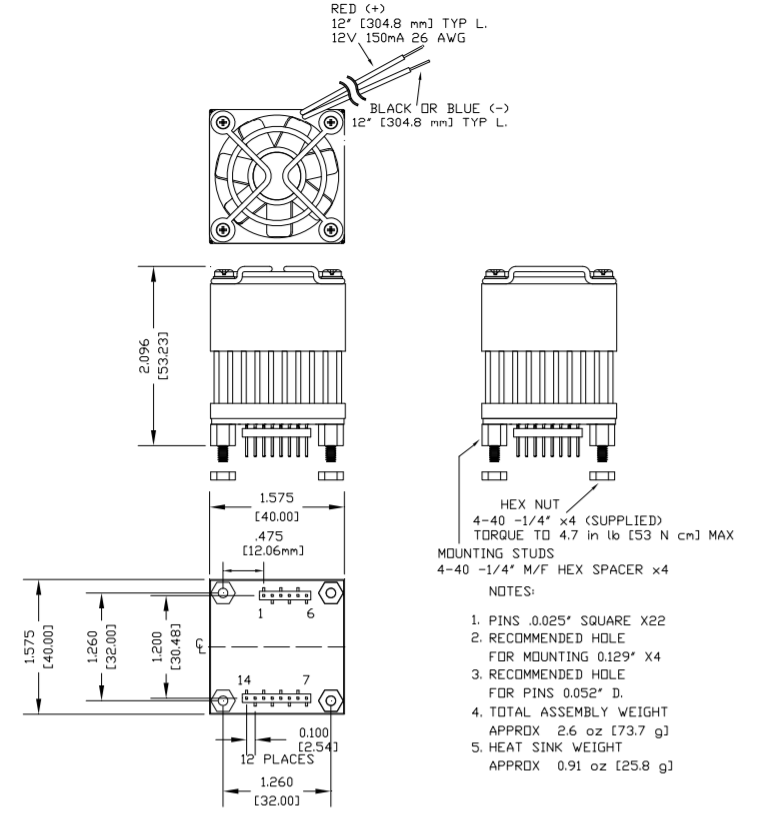
The amplifier is supplied with four 4-40 M/F hex spacers at the four corners of the amplifier. Once the amplifier is seated, secure the module with the provided 4-40 nuts and torque to 4.7 in lb [53 N cm] max. See “Dimensional Information” for a detailed drawing. It is recommended that the heat sink be grounded to the system ground. This can easily be done by providing a grounded circuit board pad around any of the holes for the mounting studs.
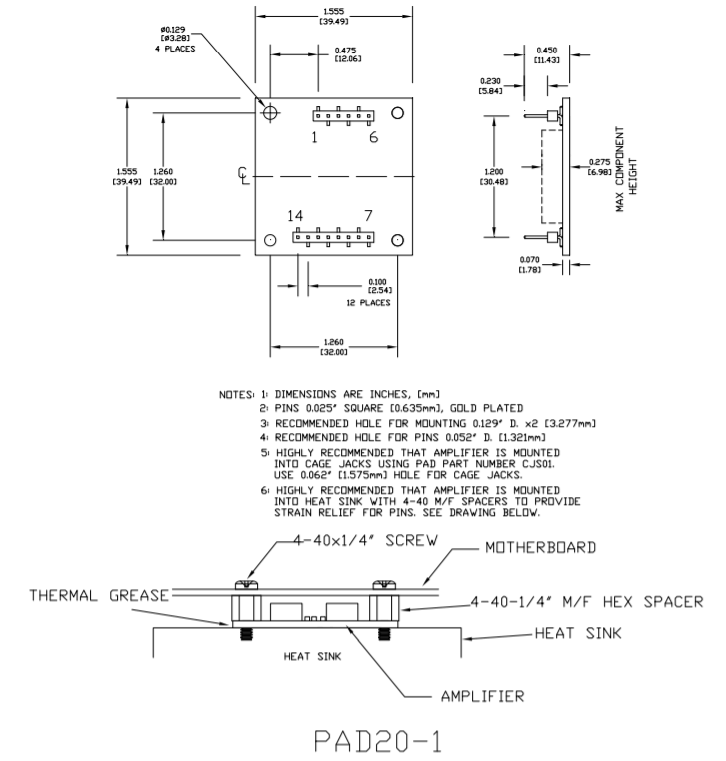
MOUNTING THE PAD20-1 AMPLIFIER
In most applications the amplifier must be attached to a heat sink. Spread a thin and even coat of heat sink grease across the back of the PAD20-1 and also the heat sink where the amplifier is to be mounted. Push the amplifier into the heat sink grease on the heat sink while slightly twisting the amplifier back and forth a few times to bed the amplifier into the heat sink grease. On the final twist align the mounting holes of the amplifier with the mounting holes in the heat sink and finish the mounting using 4-40 hex male-female spacers and torque to 4.7 in lb [53 N cm] max. Mount the amplifier to the mother board with 4-40 X 1/4” screws. See Dimensional Information for additional recommendations.
TEMPERATURE REPORTING
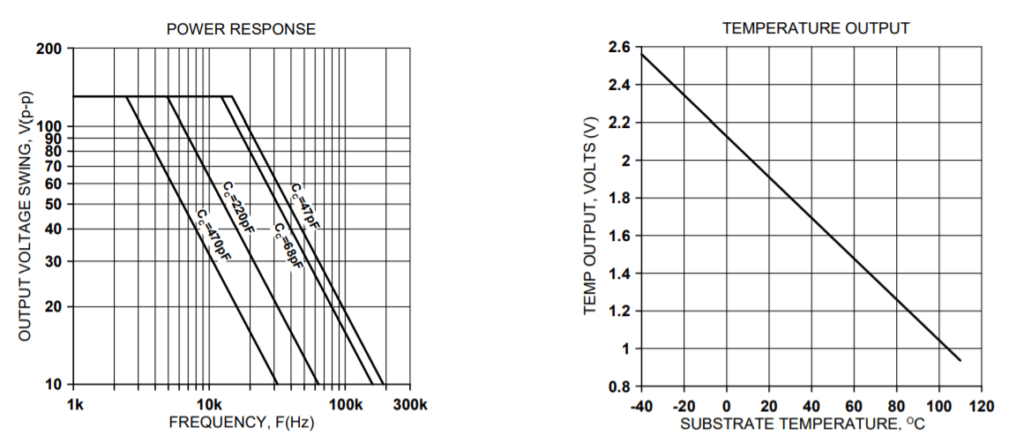
An analog output voltage is provided (pin 8, TMP) relative to ground and proportional to the temperature in degrees C. The slope is approximately -10.82mV/℃. The output voltage follows the equation:
T = (2.127 ─ V) (92.42)
Where V is the TMP output voltage and T is the substrate temperature in degrees C.
THERMAL SHUTDOWN
The temperature monitoring circuit automatically turns off the amplifier when the substrate temperature reaches 110℃. When the substrate cools down 10℃ the amplifier is enabled once again. The thermal shutdown feature is activated either by amplifier overloads or a failure of the fan circuit.
EXTERNAL SHUTDOWN
When pin 9 `( SD ) is taken low (ground) the amplifier is turned “off” and remains “off” as long as pin 9 is low. When pin 9 is monitored with a high impedance circuit it also functions as a flag, reporting when the amplifier is shut down. A “high” (+5V) on pin 9 indicates the temperature is in the normal range. A “low” (ground) indicates a shutdown condition. See Application Circuits Figure 2.
PHASE COMPENSATION
The PAD20 must be phase compensated. The compensation capacitor, Cc, is connected between pins 2 and 3. The compensation capacitor must be an NPO type capacitor rated for the full supply voltage (150V). On page 2, under Amplifier Pinout and Connections, you will find a table that gives recommended compensation capacitance value for various circuit gains and the resulting slew rate for each capacitor value. Consult also the small signal response and phase response plots for the selected compensation value in the Typical Performance Graphs section. A compensation capacitor less than 47pF is not recommended.
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE GRAPHS
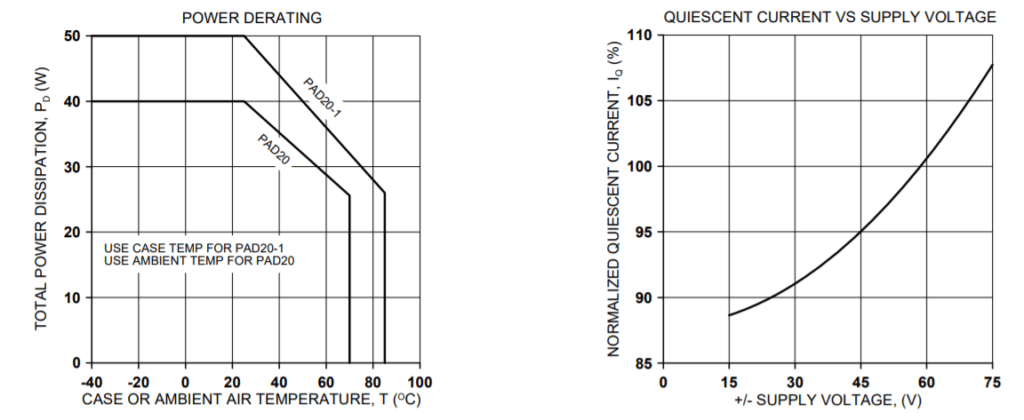
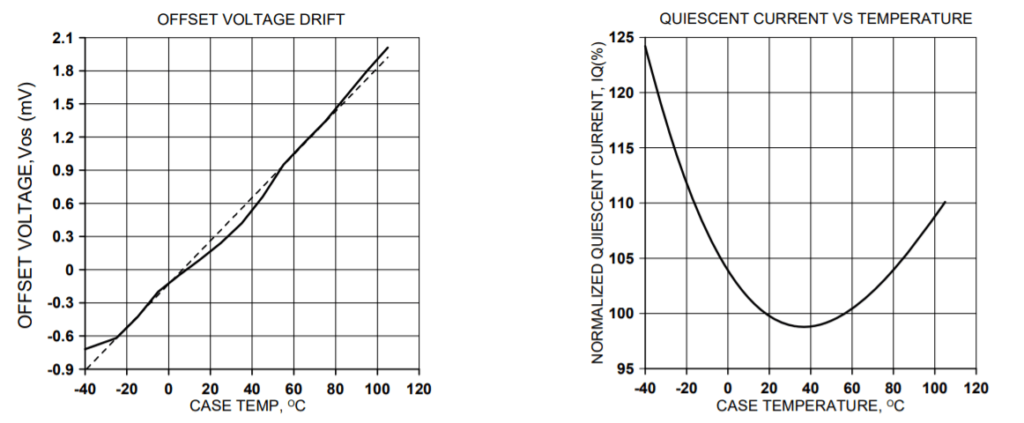
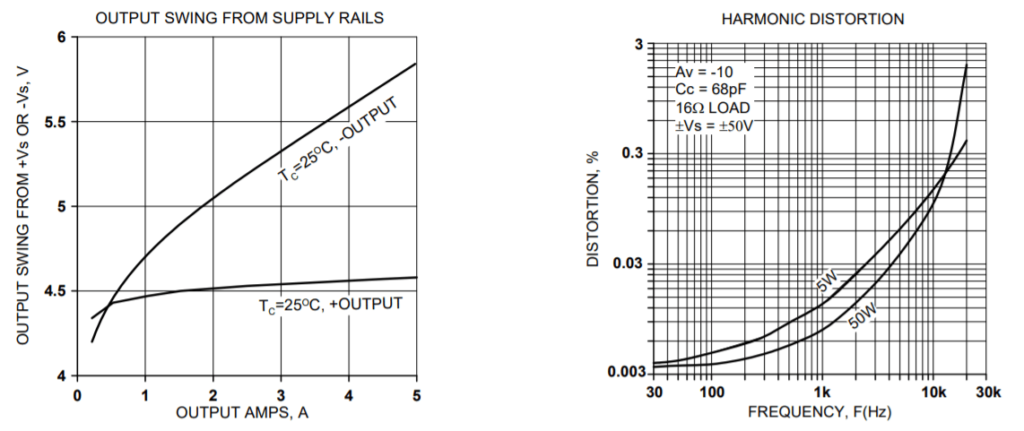
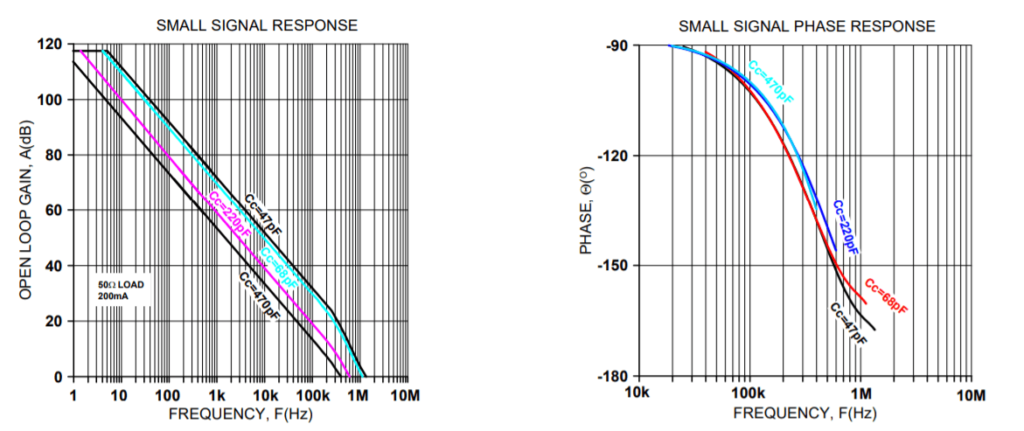
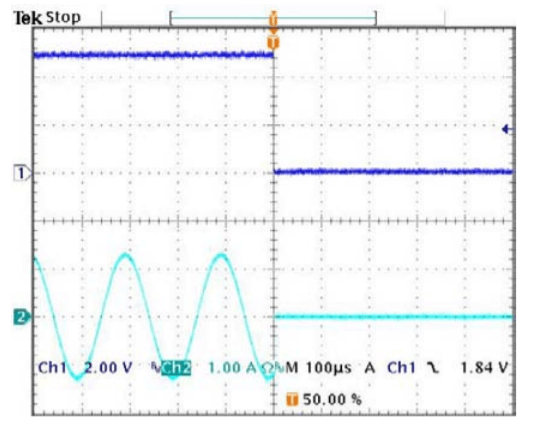
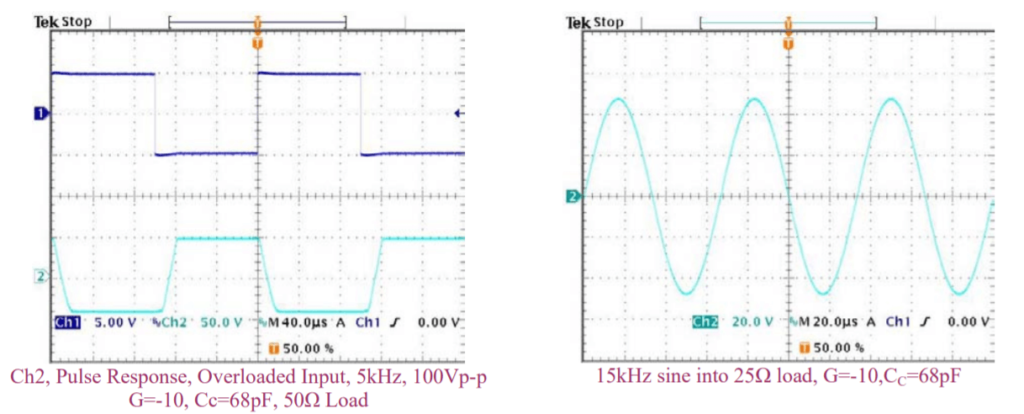
SHUTDOWN RESPONSE, NEGATIVE OUTPUT TO ZERO TRANSITION
The oscilloscope display at the left shows a view of a 5kHz, 2.5A p-p amplifier output signal being interrupted near the negative peak by a shutdown signal on Ch1. The Ch2 display shows the output current going to zero about 6µS after the shutdown signal goes low.
SHUTDOWN RESPONSE, POSITIVE OUTPUT TO ZERO TRANSITION
The oscilloscope display at the right shows a view of a 5kHz, 2.5A p-p amplifier output signal being interrupted near the positive peak by a shutdown signal on Ch1. The Ch2 display shows the output current going to zero about 40µS after the shutdown signal goes low.
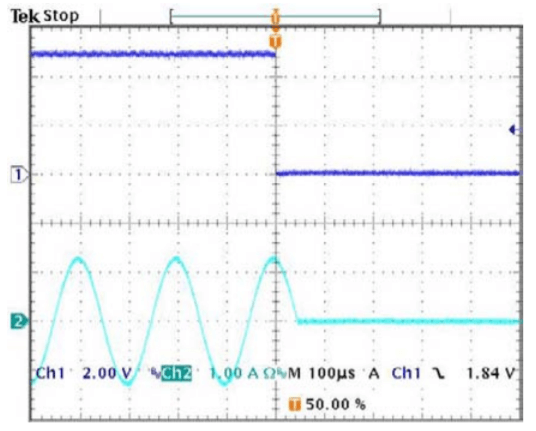
SHUTDOWN RECOVERY
The oscilloscope display at the left shows a view of a 5kHz, 2.5A p-p amplifier output signal on Ch2 resuming normal operation in the negative output direction after a shutdown signal on Ch1 go high (not shutdown). The output signal resumes normal operation after a delay of about 40µS .
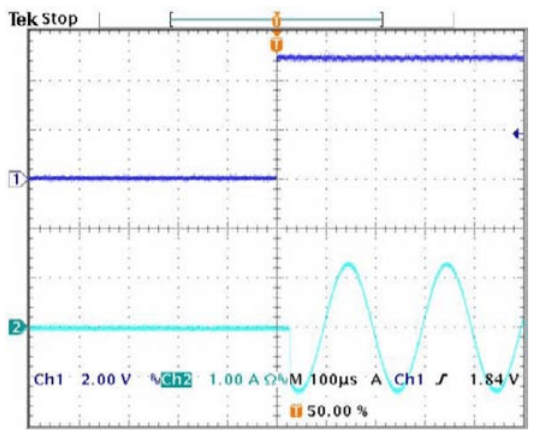
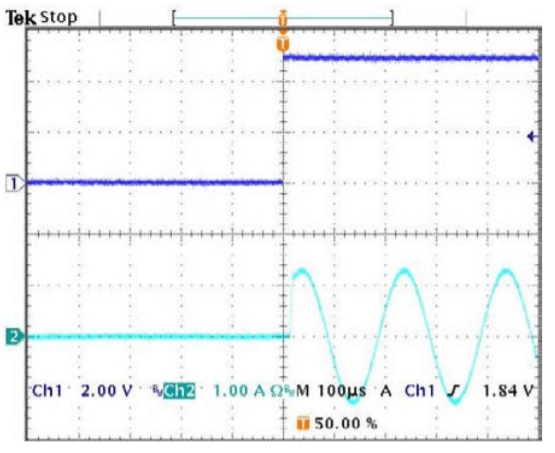
SHUTDOWN RECOVERY
The oscilloscope display at the left shows a view of a 5kHz, 2.5A p-p amplifier output signal on Ch2 resuming normal operation in the positive output direction after a shutdown signal on Ch1 go high (not shutdown). The output signal resumes normal operation after a delay of about 10µS.
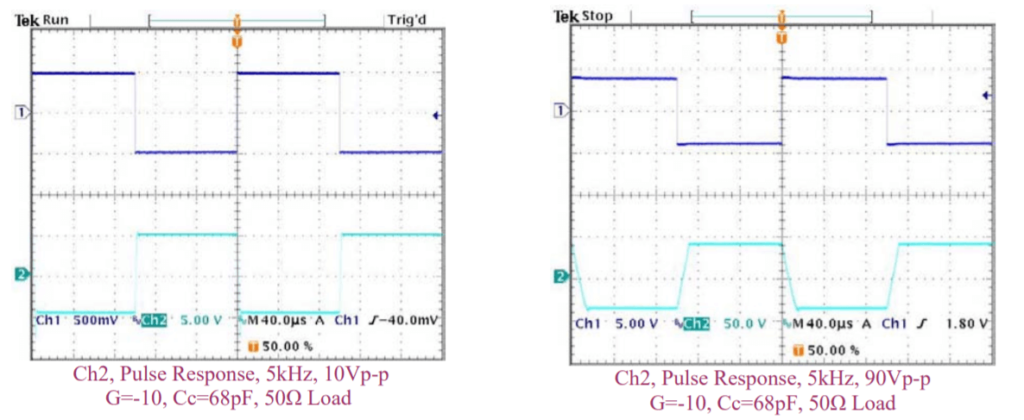
SAFE OPERATING AREA
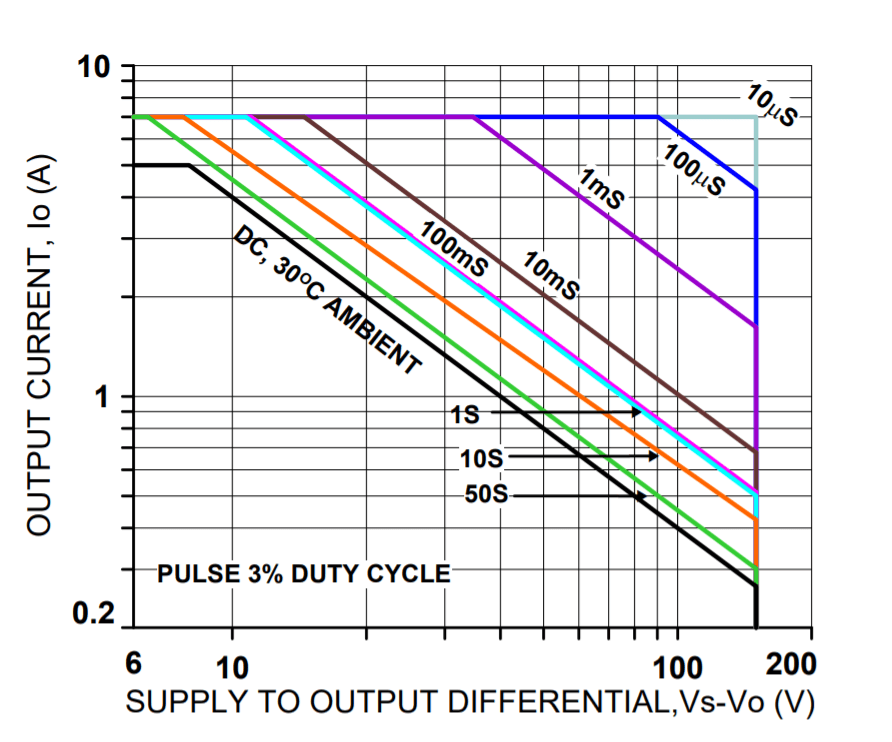
The safe operating area (SOA) of a power amplifier is its single most important specification. The SOA graph presented above serves as a first approximation to help you decide if the PAD20 will meet the demands of your application. But a more accurate determination can be reached by making use of the PAD Power™ spreadsheet which can be found in the Power Amp Design website under the Design Spreadsheet tab. While the graph above adequately shows DC SOA and some pulse information it does not take into account ambient temperatures higher than 30℃, AC sine, phase or non-symmetric conditions that often appear in real-world applications. The PAD Power™ spreadsheet takes all of these effects into account.
DIMENSIONAL INFORMATION
APPLICATION CIRCUITS
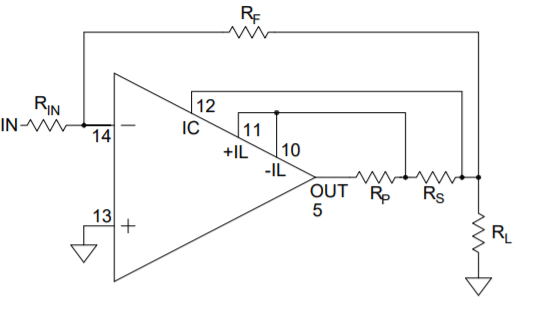
4-WIRE CURRENT LIMIT
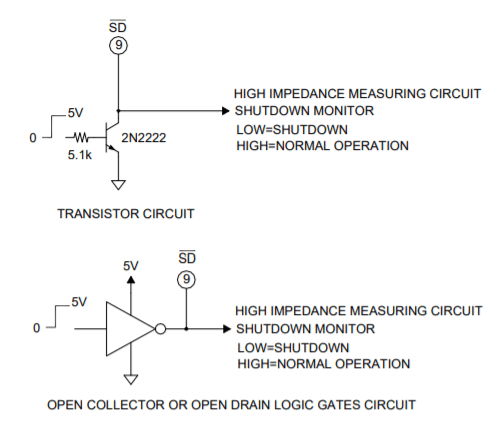
EXTERNAL SHUTDOWN WITH MONITOR
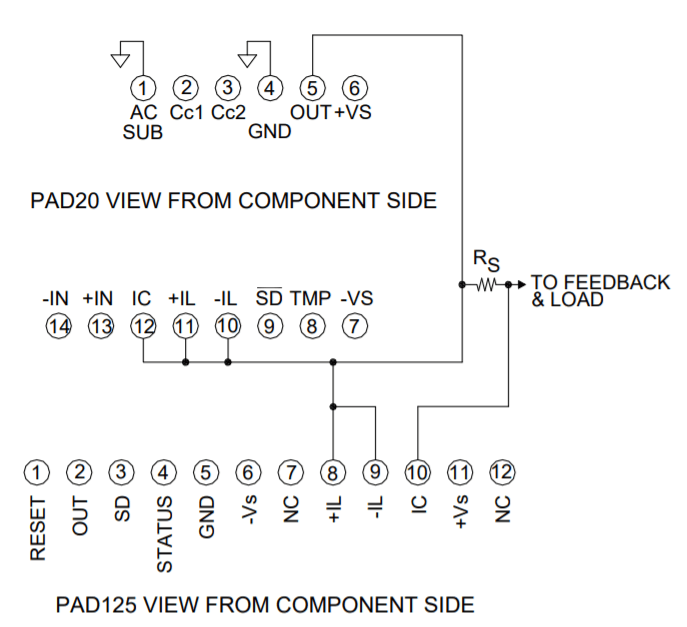
TYPICAL CONNECTIONS TO PAD125 CURRENT LIMIT ACCESSORY MODULE
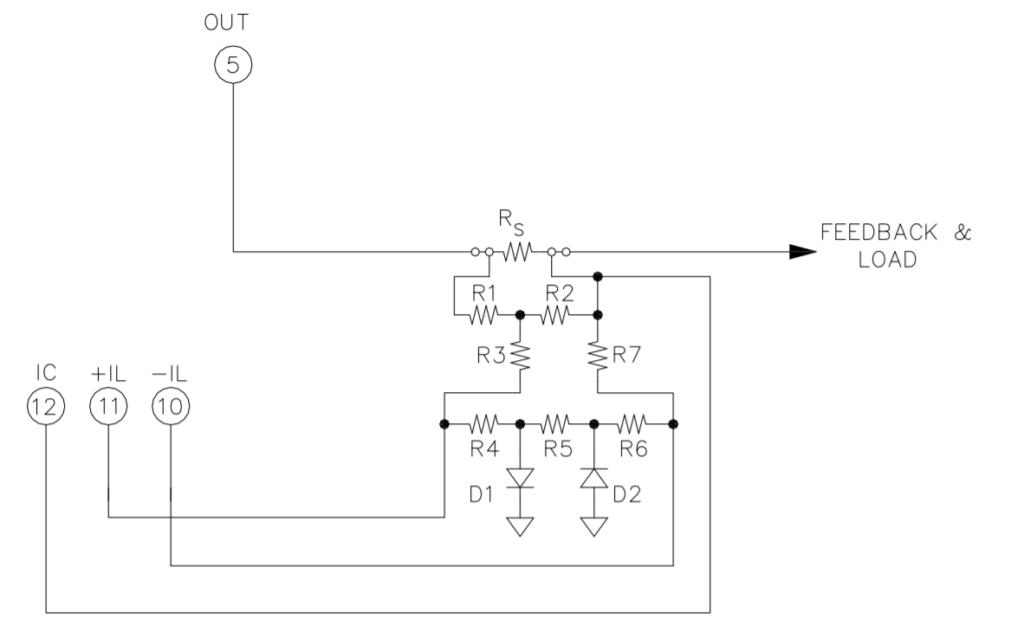
DUAL SLOPE (FOLD-OVER) CURRENT LIMIT
With the three current limit function pins (pins 10-12) dual slope current limiting can be implemented that more closely approximates the SOA curve of the amplifier than can be achieved with standard current limiting techniques. Values for resistors R1-R7 and RS can be calculated using the PAD Power™ Excel spreadsheet that can be downloaded from the Power Amp Design web site under the Design Spreadsheet tab.
